In this guide, I review the best parametric modeling software. We’ll cover both free and paid options, as well as options for amateurs and professionals, to help you find the right software for you.
Full List
- FreeCAD: Best Free & Open Source Parametric Design Software
- Fusion 360: Popular Amongst Hobbyists and Professionals
- AutoCAD: Great for 2D Parametric Modeling
- Solidworks: Powerful Software for Professional Teams
- CATIA: Most Advanced Parametric Modeling Software for Businesses
Best Parametric Modeling Software
1. FreeCAD – Best Free & Open Source Parametric Design Software
Pros
Completely free and open source
Supports BIM and finite element analysis
Strong community aspect
Can code your own parametric objects
CAM workbenches for CNC work
Cons
More limited and less intuitive than most paid software
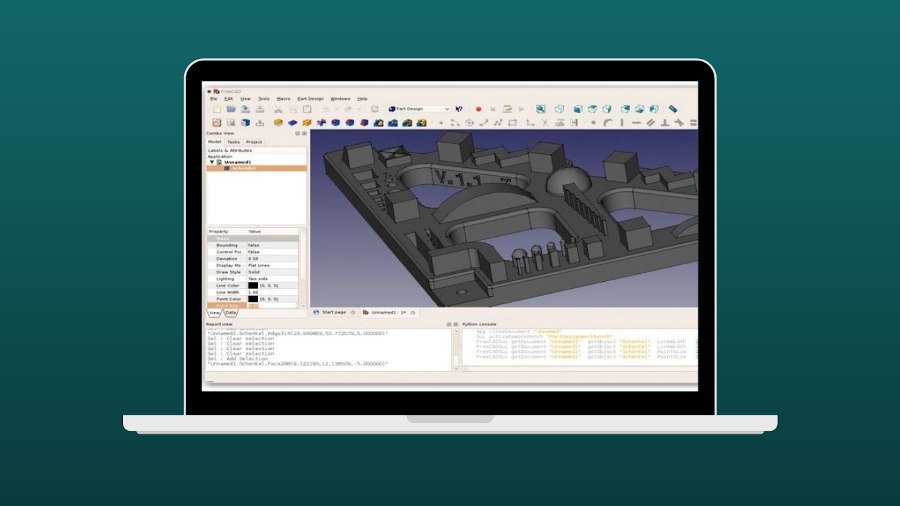
FreeCAD is the most popular parametric modeling software, and it’s completely free and open source. It’s versatile and designed to suit various applications, including mechanical engineering, product design, and architecture.
It’s based on a powerful geometry engine that uses Open CASCADE technology and supports solids, BRep objects, NURBs, and curves and surfaces. It also provides a variety of tools to create these objects, including Boolean operations and fillets.
All objects in FreeCAD are natively parametric, so you can base their shape and other features on precisely defined values, make quick and easy edits with the undo/redo stack, and create custom parametric chains defining how objects relate to each other.
One of the most impressive aspects of FreeCAD is that it supports BIM modeling and finite element analyses, typically only seen in paid software.
- FEA is particularly useful for simulating designs against real-world environments.
- BIM helps architects and engineers improve the quality and speed of design processes through centralized data management and other tools.
FreeCAD also offers a variety of CAM tools, such as workbenches, for exporting your models for 3D printing and CNC CAD/CAM software machining.
The fact that FreeCAD, unlike most parametric modeling software, is open source also brings its own benefits. For example, you can code your own parametric objects using Python.
It has a large and very active user community, and anyone with the required skills can join and help fix bugs, develop the software, and contribute to FreeCAD’s documentation. This strong community aspect is something that you don’t really get with paid parametric modeling software.
2. Fusion 360 – Popular Amongst Hobbyists and Professionals
- Price: free for hobbyists, from $70 monthly or $545 annually for a commercial license
Pros
Free for three years for hobbyists
Also free for educational use and eligible startups
Range of intuitive parametric modeling features
Also supports four other types of modeling
User-friendly with good learning support
Integrated CAM/CAE features
Specialist extensions
Cons
Limited to more basic architectural modeling
Autodesk’s Fusion 360 is another widely used parametric modeling software by both hobbyists and professionals. It’s free for three years as long as you’re not using it commercially, although there are also free licensing options for eligible startups.
Fusion 360 offers some useful parametric tools beyond those seen in most software. For example, it has highly intuitive press and pull commands that identify design features and create fillets, cut and join, or offset depending on your selected geometry.
On top of that, this software also boasts real-time downstream feature timeline changes, alongside geometry-dependent end condition creation, both of which can help improve efficiency by reducing errors.
While parametric modeling is fairly complex and requires some time to learn, Fusion 360 is one of the most intuitive and beginner-friendly options. Autodesk provides great support as well as tutorials to help you learn how to parametrically model using this software, and there’s also loads of YouTube videos on the subject. I personally prefer to model parts for CNC and 3D printing in Fusion 360, but that’s just my personal preference.
Fusion 360 is one of the most versatile 3D modeling software, as it supports direct, surface, freeform, and mesh modeling as well as parametric. You can learn more about this in our Fusion 360 vs FreeCAD guide, where we compare the various modeling tools each offers.
It’s also the only platform with cloud-integrated CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB capabilities. It’s primarily aimed at mechanical engineers, industrial designers, and electronics engineers, but it’s also used for basic architectural modeling.
There’s also extensions for machining, product design, generative design, and nesting and fabrication. So, overall it’s a fairly customizable tool and allows you to start for free and gradually build up depending on what you need.
3. AutoCAD – Great for 2D Parametric Modeling
- Price: from $235 per month
Pros
Excellent for 2D parametric drafting (also supports modeling)
Widely used by architects and engineers
Specialized toolsets for seven applications
Proven in case studies to improve efficiency
Mobile app for on-the-go editing
Highly intuitive and customizable interface
Cons
More geared towards 2D than 3D
AutoCAD is another Autodesk software that’s among the most popular 2D and 3D CAD programs.
It’s more versatile than Fusion 360 in that it’s better optimized for professional use in applications like architecture. In fact, there are seven included tool sets in AutoCAD for architecture, mechanics, electronics, MEP, 3D maps, plants, and raster designs.
These tool sets can greatly improve your efficiency. One study found the architectural toolset boosted productivity by up to 61%, while a similar study found it boosted productivity by up to 55%.
Although it offers various types of 3D modeling, AutoCAD is best known for its range of powerful 2D drafting tools, which include parametric drafting. These parametric drawing tools let you set dimensional constraints on individual objects, and geometric constraints on how objects relate to each other.
You can then automate tasks by instantly applying multiple geometric constraints to objects and easily make design changes by editing the variable values. You can also use formulas and equations to further streamline your parameter management.
AutoCAD’s collaborative cloud features, such as the ability to easily share and reuse data from PDFs by attaching them as underlays, are useful for team collaboration. There’s also an iOS and Android app for easily viewing, sharing, and editing AutoCAD drawings.
AutoCAD is a highly customizable CAD/CAM software, as it allows you to modify the interface with APIs as well as a variety of add-on apps and plugins for configuring your user experience to your preferences.
4. Solidworks – Powerful Software for Professional Teams
- Price: upon quote
Pros
Wide range of advanced parametric modeling tools
Integrated CAD, CAM, and CAE
Can improve efficiency by up to 20%
Proven to help reduce design and manufacturing costs
Customizable and configurable packages are available
Solutions for a variety of different industries
Centered on collaboration
Cons
Difficult to learn
Not available on Mac
Solidworks, by Dassault Systemes, is one of the most advanced parametric modeling tools – aimed at professional engineering and mechanical modelers, rather than hobbyists and amateurs. It’s excellent, but with heavy depth and detail: there’s an entire 16-module book for learning its parametric modeling.
If you do learn it, though, you have a seriously powerful piece of software on your hands. Unlike Fusion 360, which supports various types of modeling, Solidworks is a true parametric tool.
This parametric modeling software is designed primarily for mechanical engineering and industrial designers. It also provides a wide variety of CAD, CAM, and CAE tools, making it a complete solution for anyone working within these industries.
One of Solidworks’ main selling points is its ability to improve efficiency – case studies have shown it can reduce revision errors by up to 20%, for example. There’s cloud-based modeling and other collaborative tools to improve teamwork, and it can help to validate designs earlier and reduce costs thanks to its advanced simulation, manufacturability checks, and cost estimates.
Unlike the software we’ve covered so far, it’s not as simple as just paying the fee and downloading Solidworks. This is an upon-quote solution in which you select the specific Solidworks products based on your needs. You also have to buy it from a distributor.
This includes custom solutions for startups and companies operating in defense, industrial equipment, healthcare, infrastructure, and many more industries. There’s also educational solutions for teachers, researchers, and students.
5. CATIA – Most Advanced Parametric Modeling Software for Businesses
- Price: upon quote
Pros
The most powerful parametric modeling software
Huge range of tools and products
Highly configurable and flexible
Widely used in industrial design
Large professional user network
Lots of extensive learning resources including e-seminars
Cloud-based with integrated collaborative tools
Cons
Too expensive and complex for most amateurs
Not available on Mac
CATIA is another complex and extremely powerful parametric modeling software from Dassault Systemes widely used by professional modelers.
Like Solidworks, CATIA is designed for businesses and can’t be downloaded after paying a set price – you need to contact the sales team to get a custom quote.
Expect to pay over $10,000 a year for a full license, whereas Solidworks is more around the $3,000-$5,000 mark. You can check out our CATIA vs Solidworks comparison to learn more about how these two programs compare.
CATIA is actually a software suite rather than a single standalone software. The full version is CATIA V5, which offers a wide range of different capabilities. These include specification-driven mechanical design, product synthesis and analysis, collaborative product creation and data management, and much more.
Alternatively, you can purchase individual CATIA products, referred to as “roles” for specific tasks in engineering, systems engineering, design, construction, product development, and structures. There are also educational modules.
For example, there are individual CATIA products for designing composite parts, mechanical boat modeling, and engineering thermal systems. There are also tools designed to help improve productivity, such as the Systems Solutions Architect which can reduce design times by providing consistent product definitions.
They only touch the surface of the huge range of parametric modeling tools available at CATIA, but it’s a very flexible product and you can pick and choose the specific products you need.
What is Meant By Parametric Modeling?
Parametric modeling is a form of 3D modeling in which models are built upon pre-programmed rules or algorithms known as parameters. These define the nature of objects as well as how objects relate to each other.
This has several benefits, including high accuracy and efficiency, and parametric modeling software is widely used in fields like mechanical design engineering.
Pros and Cons of Parametric Modeling
Pros
Accurate
When 3D modeling is based on parameters, your model won’t deviate from the parameters such as dimensions or curvature, and constraints that you set. This helps preserve design intent. Parametric design software also provides geometric control features for maintaining high levels of precision.
As you’re not manually manipulating a model and its elements, you can reduce the level of human error compared to direct modeling. This is why parametric modeling is widely used for highly complex and technical designs where high precision is vital, such as industrial design, mechanical engineering, and architecture.
Fast
Parametric modeling can speed up the modeling process as you can instantly update all aspects of a model by changing the parameters. Also, you can modify entire shapes at once, rather than just individual aspects of models.
For example, imagine you’re an architect designing a roof. If you’re not modeling parametrically, you’ll need to change the width, breadth, and height to change the roof’s structure. With parametric software, you just need to change one, and the others will automatically update.
Parametric modelers allow you to view how such modifications affect a model in real-time, and automate repetitive changes by defining rules on how different design elements interact.
Cons
High skill level required
Parametric modeling is a fairly complex process with a steep learning curve. It requires time and patience to build up your skills, and the most advanced software, like Solidworks and CATIA, are not suitable for beginners or even immediate modelers without serious training.
Less flexible
Another downside to parametric modeling’s more mathematical approach is it can take longer to get started with, and is less flexible than other forms of modeling.
For example, direct modeling is generally more flexible, as you can quickly create and change geometry-based models simply by manually manipulating them.
What to Consider When Choosing Parametric Modeling Software?

Ease of use
Parametric modeling has a fairly steep learning curve, although some programs are more beginner-friendly than others. Fusion 360 is particularly beginner-friendly yet still powerful, while FreeCAD and AutoCAD are also worth considering for amateurs learning the ropes.
On the other hand, more advanced and complex programs like Solidworks and CATIA have significantly steeper learning curves and are used by professional modelers.
Compatibility
It’s also important to ensure that your parametric design software is compatible with your preferred operating system. FreeCAD is one of the few that’s available on Windows, Mac, and Linux, whereas other software may not.
For example, AutoCAD and Fusion 360 are both available on Windows and Mac but not on Linux. Then you have CATIA and Solidworks, which are only compatible with Windows.
Some parametric modeling software that run on Mac haven’t been updated to run natively on Apple’s latest M1 and M2 silicon chips. While some, like AutoCAD’s latest versions, have, for others you’ll need to use Rosetta 2, which can impact performance.
Support
As parametric design is a fairly complex and skilled process, strong customer support, training resources, and documentation, are essential – especially for beginners.
The type and level of support you get can vary depending on the software. For example, as FreeCAD is open source, you rely on the community for support. You can still reach out to developers and contributors, but you’re not going to get a professional support service like paid software offer.
The likes of Fusion 360 and AutoCAD offer good support and also have community forums where you can post questions to other users. Then you have the likes of Solidworks and CATIA, which provide the highest level of customer and technical support for teams and businesses.
Cost
The price of parametric modeling software varies widely, from completely free solutions like FreeCAD, mid-range options like AutoCAD, to premium software like Solidworks and CATIA that cost thousands of dollars.
The latter two don’t even advertise any prices on their site – you need to request a quote based on your specific need and configurations.
However, Solidworks starts from at least $4,000-$5,000, depending on whether you’re going for a Standard or Professional License, while a fully functional CATIA license costs over $10,000. Both also have yearly maintenance fees of $1,000-$2,000.
Customizability
Most parametric software are customizability to an extent, but this extent differs. For example, Fusion 360 offers various extensions that you can add for more design tools, whereas AutoCAD has a wide variety of plugins available and a highly customizable interface designed for you to streamline your user experience to your liking.
Technically, open-source programs like FreeCAD offer the most customizability, as if you have coding skills, you can expand the software and add your own features. However, most 3D modelers won’t have these skills.
Professional programs like Solidworks provide customizability in a different way, as you can choose from the huge range of tools and products on offer rather than buying a whole singular package. This helps prevent you from spending money on tools you don’t need, while also streamlining and improving your overall user experience.
FAQ:
Who uses Parametric modeling software?
Parametric software is widely used in industries where high precision and efficiency are priorities, such as mechanical engineering and architecture.
Parametric modeling vs nonparametric modeling
Parametric models are based on predefined parameters, such as dimensions, features, and constraints. Nonparametric (direct) modeling is a more flexible and manual approach that lets you quickly define and manipulate geometry.
What is parametric modeling, and how is it different from other types of 3D modeling?
Parametric modeling is a mathematical approach to 3D modeling in which models are defined by features, dimensions, and constraints. It’s typically more precise and allows for more automation than other types of 3D modeling, like direct modeling, which is a more flexible geometry-based method.