Key Takeaways
- Laser Beam Generation: A laser cutter uses a laser diode, CO2 gas, or fiber optic cable to produce a high-powered laser beam.
- Laser Beam Control: A laser cutter uses mirrors and lenses to focus and direct the laser beam onto the material, following computer instructions.
- Laser Cutting Process: A laser cutter melts or vaporizes the material with the laser beam, creating precise and complex cuts or engravings.
- Laser Cutter Types: There are three types of laser cutters: diode, CO2, and fiber. Each has different power, speed, and material compatibility.
A laser cutter is a machine that uses a laser beam to cut or engrave materials such as wood, plastic, or metal. It works by directing the laser beam through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus the energy onto a small spot, melting or vaporizing the material based on instructions from a computer.
In this article, I’ll explain how laser cutters work, the main types of laser cutters, their applications, and laser cutting pros and cons versus other options.
Also, if you’re thinking of buying your own laser cutter, I’ll share a few tips and things to consider when purchasing.
How Does a Laser Cutter Work?
A laser cutter works by using a high-powered laser beam to cut or engrave materials with high precision. The process is controlled by computer software, and the laser beam is focused and directed onto the material, which causes it to heat up and vaporize or melt, creating precise cuts or etchings.
A laser cutter consists of two systems: one produces the high-powered laser beam, and the other moves the laser head with a computer (computer numerical control).
The light of a focused laser beam has two properties:
- The laser beam light rays are focused on a spot.
- The laser beam light rays have similar waves (they start vibrating together and with the same frequency – monochromatic light).
A laser cutter uses mirrors and lenses to direct the lights into a focused spot. Then, it uses a laser generator to produce light rays.
Types of Laser Cutters
There are three types of laser cutters: diode lasers, CO2 lasers, and fiber lasers.
Diode
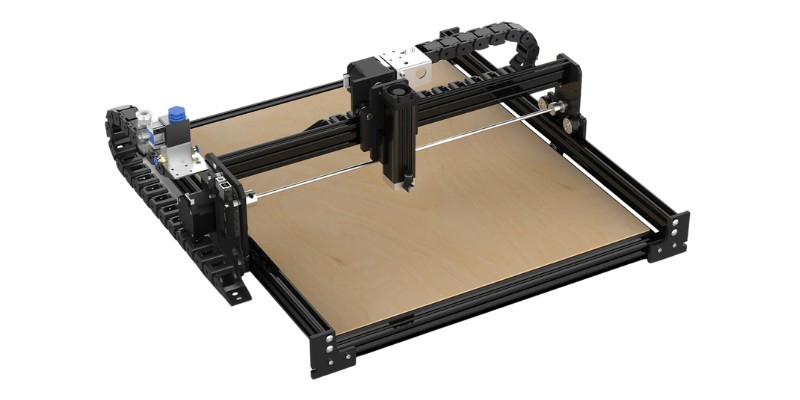

Diode laser cutters use a laser diode to generate the light. This laser technology is similar to an LED, with the difference that it creates a laser beam when excited with electricity.
Here are the main characteristic of diode lasers:
- Cheapest: prices between $200-$1500
- Weakest: power ranges between 1W-40W
- Slowest: slowest type of laser
- Materials they can cut: wood, dark acrylic, cardboard, paper, felt.
- Materials they can engrave: slate, dark glass, steel, and anodized aluminum
This type of laser cutter is excellent for hobbyists since they’re cheap, and easy to use. However, they have low laser power and can’t cut as thick as a high-power laser. These laser cutting machines are not fast either, and require more passes, and slower speeds, to cut through materials that other laser types can do much faster.
CO2
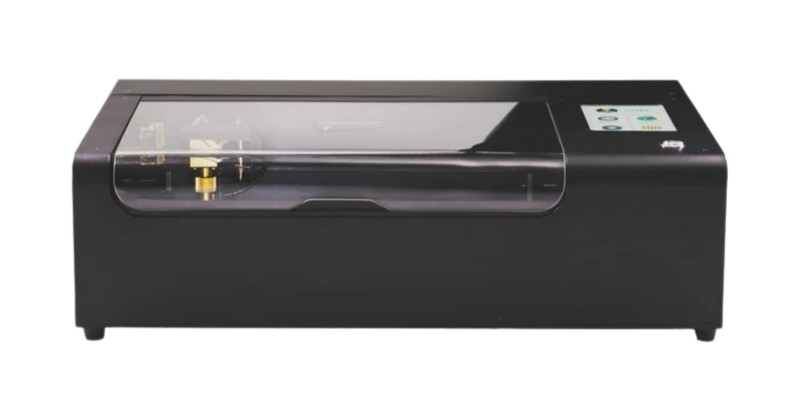

A CO2 laser cutter is a gas laser. A gas laser cutter has a gas tube that contains carbon dioxide (CO2) with other gases. When electricity excites the carbon dioxide, it emits a laser beam with the second property we mentioned earlier.
The main things you need to know about CO2 laser cutting are these:
- Entry-level power ranges: between 30W-300W (industrial CO2 lasers can reach 15000W)
- Entry-level price ranges: between $500-$7000
- Compatible materials: wood, acrylic, leather, foam, glass, rubber
A CO2 laser is excellent for hobbyists and small businesses. It can cut and engrave the widest range of materials (but, not metals). They can even laser cut clear acrylic, which diode lasers can’t do, as they are limited to dark colors of acrylic.
Hobbyist CO2 lasers are relatively cheap and offer great performance for their price. Suitable lasers for small shops and hobbyists generally cost $500 to $7,000, and for example, a 50W CO2 laser with cameras can cost as low as $3,000.
Fiber
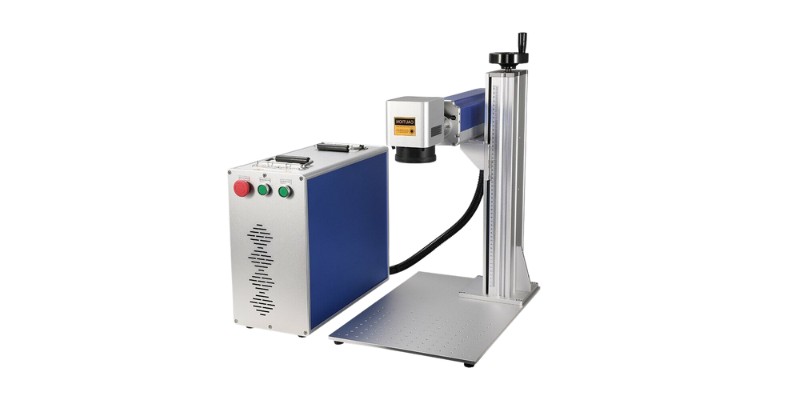

A fiber laser cutter is a type of laser cutter that uses fiber optic cable to generate a laser beam. It is known for its high precision and speed, making it ideal for industrial applications. When the fiber optic cable is excited with light, it responds by producing laser light.
Fiber laser cutters are capable of cutting through a variety of materials, including metals, with great accuracy.
A fiber laser cutter can also mark metals, which is a unique form of engraving that other laser cutters can’t do. In laser marking processes, a fiber laser cutter makes the metal surface react with oxygen and change colors to reveal the marking. Its benefit is not interfering with the top layer.
These are the main characteristics of fiber laser cutters:
- Entry-level power: ranges between 10W-100W
- Entry-level price: ranges from $2,500 to $10,000 (industrial machines can cost $300K+)
- Materials they can cut: metals like gold, silver, steel, bronze, nickel, aluminum, etc
- Materials they can engrave: acrylic, stones, hard plastics, and metals
However, fiber laser cutters don’t enjoy the material diversity that CO2 lasers have. For example, laser cutting wood is not advisable with a fiber laser, as they give poor surface finishes on wood, and can set the wood on fire.
Starting in around the 40W range, fiber lasers begin being able to cut extremely thin metals, of around 0.15mm in thickness. This makes them ideal for marking metals, or cutting jewelry patterns out of thin plates.
For example, you can cut your name out of a thin gold plate with a fiber laser cutter. For this reason, entry-level fiber laser cutters have a small work area (about 7″ by 7″).
MOPA Fiber Laser Cutter
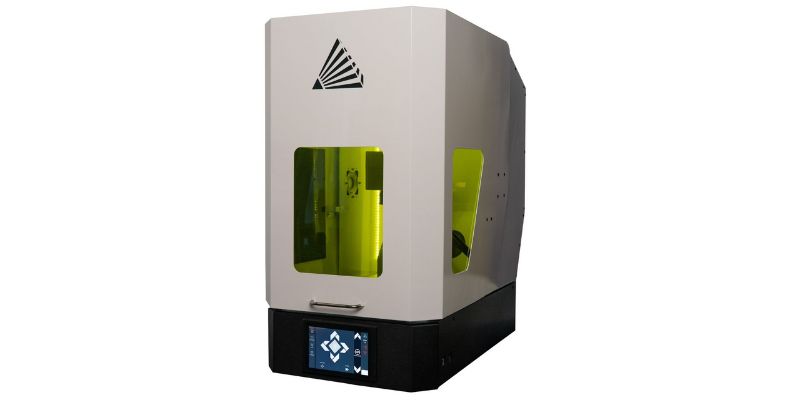

MOPA fiber laser cutters can send a pulsed laser beam, meaning they can mark metals in color Those who need to put colored logos on metal parts will need a MOPA fiber laser cutter. We’ve explained every method for laser engraving with color here.
Applications: What Is a Laser Cutter Commonly Used for?
- Making arts and home decorative paraphernalia
- Customizing objects by engraving or custom cutting
- Prototyping
- Jewelry making
- Printing product info and logo
- Cutting process of various materials in industries (automotive, medical, sports, etc.)
- Sheet metal cutting process (industrial)
- Welding
Pros and Cons of Laser Cutting
Pros
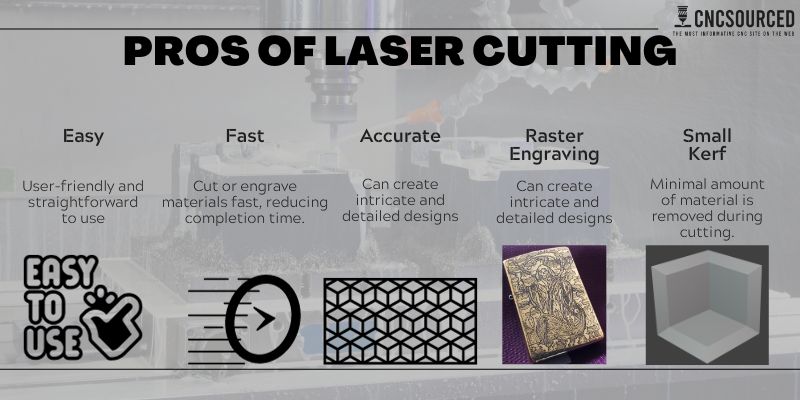
- Easy: Laser cutters are user-friendly and straightforward to operate.
- Fast: Laser cutters can swiftly cut or engrave materials, reducing production time compared to traditional methods.
- Accurate: With precise laser beams, laser cutters can create intricate and detailed designs.
- Raster engraving with high resolution: Laser cutters can engrave images or text with excellent clarity and resolution.
- Small kerf: Laser cutters remove a minimal amount of material during the cutting process, resulting in clean and precise cuts without excessive waste.
Cons
- Material thickness: can’t cut as thick as plasma cutting
- Higher operational costs than plasma cutting
- Not compatible with some materials: can’t cut PVC, some foams, some plastics, stones
- Only a 2D technology: unlike CNC machines which can use multiple axes to cut from angles.
- Mostly suitable for sheet material
Software
Laser software controls the operation of a laser cutter. It allows users to create and edit designs, adjust settings such as power and speed, and send instructions to the laser cutter.
CNC laser cutting involves two types of software:
- Laser control software
- Laser design software
We have written an in-depth article recommending our top laser cutter software.
What Is a Laser Cutter Control Software?
This is the software that runs the laser. You’ll import images for engraving and ready designs from the internet or your own design for cutting. Lightburn is the most popular control software that’s compatible with most laser cutters.
What Is a Laser Cutter Design Software?
Laser cutter design software is what you use to create your own artistic designs. It’s not essential for the CNC laser cutting process, since you can download and use existing images without any prior design skills.
Adobe Illustrator, CorelDraw, and Inkscape are the most popular laser cutter design software.
Buying a Laser Cutter
- Choose a laser type based on material compatibility: fiber laser for metals and CO2 or diode laser for non-metals. You can read here to compare CO2 lasers and fiber laser cutters.
- Determine your laser power needs and work area
- Consider ease of use: does it have cameras, autofocus, etc?
- Capabilities: does it have a camera, passthrough slots, rotary compatibility, etc?
- Price: does the price match the laser cutter’s capabilities and your budget?
For our current top recommendations, I recommend reading our guide to the best laser cutters and engravers.
FAQs:
What is the difference between laser cutting, engraving, etching, and marking?
Laser cutting involves fully cuts through the material thickness. Laser engraving vaporizes the surface to create cavities. Laser etching melts the surface for a contrasting pattern. Laser marking creates marks through localized heating while preserving the surface.
We also have articles explaining all the differences between laser engraving, laser etching, and laser marking and another article talking about the main types of CNC machines.