Key Takeaways
- Engraving Methods: Raster engraving scans the material line by line, while vector engraving follows the outlines of shapes.
- Engraving Results: Raster engraving creates images with shading and gradients, while vector engraving creates sharp and clean lines.
- Engraving Speed: Raster engraving is slower than vector engraving, as it covers more area and requires more movements.
- Engraving Applications: Raster engraving is ideal for photos, logos, and text, while vector engraving is suitable for cutting, scoring, and marking.
Not sure whether to use raster engraving or vector engraving in your next laser project? Or what the exact differences are?
Having used both extensively during my laser cutter tests for CNCSourced, I’ll try to help explain the differences in this article, as well as their pros and cons.
A Quick Summary
Raster engraving and vector engraving both have the capabilities to suit different applications. Here’s a quick summary:
- Raster files are images and pictures that use pixels and bitmaps (like images from your camera phone), while vector files are scalable as they use mathematical formulas instead of pixels.
- Raster engraving is similar to printing a picture, whereas vector engraving is similar to drawing outlines with a pen.
- Vector files can be used for laser cutting and engraving, but raster files can only be used for engraving.
- Vector engraving is suitable for engraving precise and detailed line drawings and outlines, whereas raster engraving is better for engraving images with shading and color contrasts, or for filling larger areas with patterns or textures.
- Raster engraving can print greyscale images, but vector engraving cannot.
- Vector engraving engraves perfect curves without any gaps, but because raster engraving uses pixels, there are tiny gaps within curves.
- Raster engraving is bolder; vector engraving is finer.
- Although the laser moves much faster in raster engraving, raster engraving is slower than vector engraving, because raster engraving covers more area and fills in images and shading.
What is Raster Engraving?
Raster engraving is an engraving method that uses a laser to burn designs onto your desired material’s surface based on pixels.
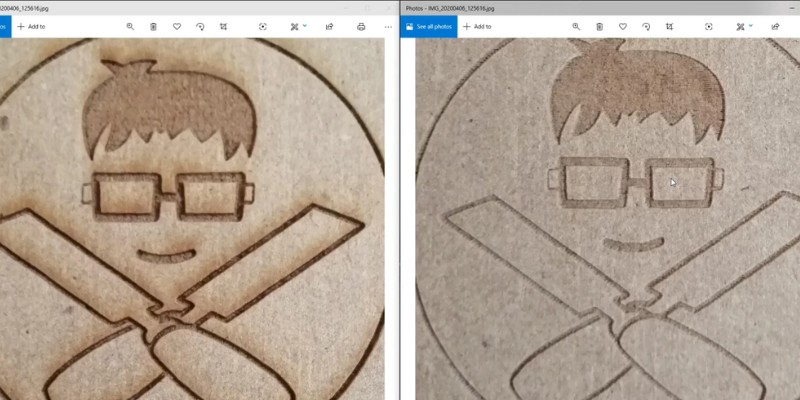
The laser head moves across the surface of the material in a series of parallel lines. This creates a rasterized image made up of a series of dots.
Raster engraving can be used on a variety of materials. Its versatility allows for the creation of contrasting, textured designs depending on how dark you burn the material in different areas.
Common raster file formats include JPEG, PNG, BMP, HEIC, EXIF, WebP, PSD, TIFF, and more.
It is a quick engraving process that can produce a high volume of orders in a short space of time. It is also relatively straightforward – just import any image (most image file formats are compatible with most laser engraving software) and send it to your laser to engrave.
What is Vector Engraving?
Vector engraving uses a vector file to direct a laser head. Vector files use mathematical formulas to direct the laser to cut precise lines that do not lose quality (or become “pixelized”) as you scale the design up or down.

This makes vector engraving ideal for engraving precise designs, such as writing text outlines or creating logo outlines. Vector engraving produces a sharp, clean finish for a professional, polished look, and scale perfectly, no matter how large the design.
Common vector file formats include SVG, AI, PDF, DXF, and EPS.
Because it requires design or vectorization, specialist software is required to design these files. Adobe Illustrator is a widely-used professional option, but open-source free software for designing vector SVG files exist, such as Inkscape.
Here’s How Vector and Raster Engraving Are Different
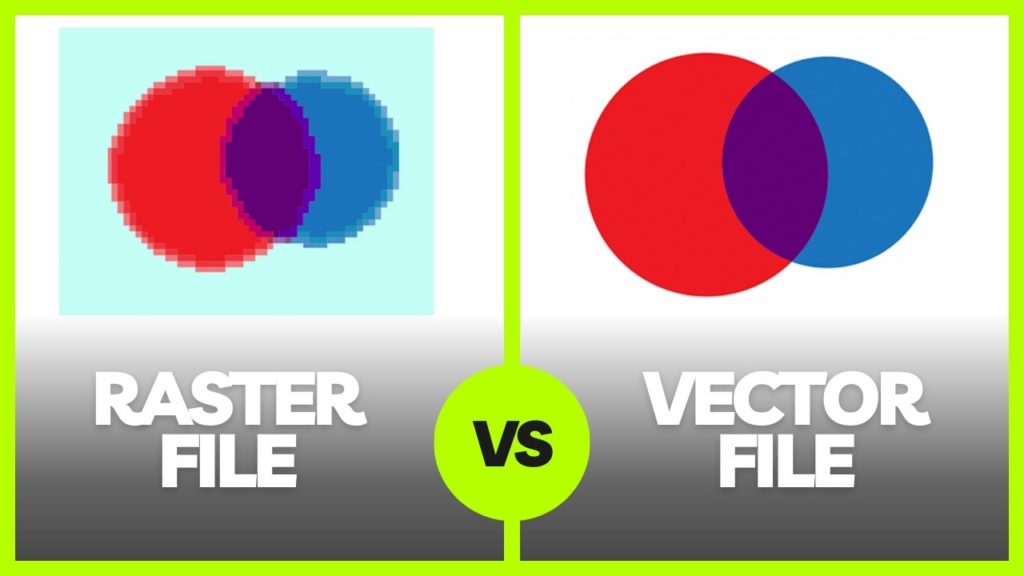
The two main differences between vector and raster engraving are how the designs are created, and how the laser marks materials.
Vector designs use mathematical formulas that laser heads trace, creating a very precise cut or engraving on the material.
On the other hand, raster images use pixels, burning these dots into the material to create the final design. This works similarly to how inkjet printing uses pixels to print on paper.
The raster image is created by the laser or engraving head moving across the material in parallel lines (a raster pattern).
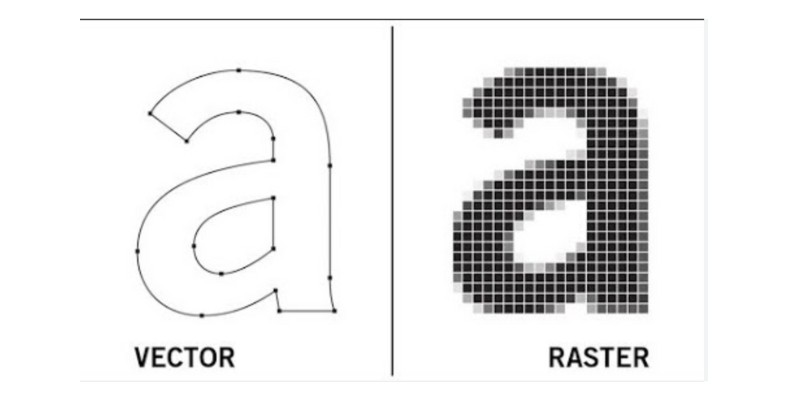
By moving the laser back and forth in this raster pattern, you can create shading, gradients, and intricate details. Raster engraving is commonly used for engraving photos, complex artwork, or any other design that requires varying depths and textures. However, it tends to be slower as it scans the entire image area pixel by pixel.
Vector engraving is better for fast engraving of fine drawings, while raster engraving is excellent for printing images and logos with filled or greyscale contrasting areas.
We also published an article discussing the differences between hand engraving vs laser engraving as well as the pros and cons of each.
Pros and Cons of Vector Engraving
Pros
- Precision – Vector files are perfectly accurate for curves and other details, and when combined with a computer-controlled laser that can follow these instructions to within a fraction of a millimeter, you get access to very high precision. This also makes it ideal for larger projects where raster images may lose resolution and pixelate. Vector files are preferred for vinyl cutting and printing on t-shirts for this same reason.
- Laser Cutting – You can laser cut materials with a vector file, but you can’t cut with rasters.
- Speed – You can quickly cut with vectors, without a drop in quality.
Cons
- Limited depth – vector engraving can’t reflect image depth, whereas raster engraving creates 3D effects in the image using color contrast.
- Limited texture – Vector engraving results in a smooth surface. So, for a varied and textured finish, you’ll want to opt for raster engraving.

- Limited colors – Vector engraving is typically a one-color process. This can limit designs.
- Complexity – Vector engraving requires more specialized software than simple JPEG images for raster engraving. Vector design software like Inkscape or Adobe Illustrator are required.
Pros and Cons of Raster Engraving
Pros
- Versatility – Like vector engraving, raster engraving can also be used on a range of materials. This includes metal, plastic, and wood.
- Texture – Raster engraving can provide a range of textures which makes it great for different applications, and give designs an artisanal feel. This can add dimension to designs.
- Full color – You can engrave dark or light shades, based on how quickly and at what power your laser burns any particular area of the image. This makes it ideal for high-quality greyscale image engraving.
- Cost-effective – The simplicity and speed of raster engraving can make it easier to produce large quantities of engraved products. This makes raster engraving a potentially very profitable business – hence the number of Etsy stores that now sell custom laser engraved goods.
Cons
- No cutting – You can only engrave with a raster file, not cut.
- Slower – although the laser is faster in raster engraving, the process is generally slower because a lot more area needs to be covered, and you’re shading and filling in the image, not just cutting the outside as with vector engraving.
- Lower precision – Raster engraving is typically not as precise as vector engraving. This isn’t just because raster files don’t scale perfectly either, it’s also because if you’re using a lower DPI image, it’ll come out looking rough.
- Images lose quality when scaled up – Enlarging designs lose resolution and quality.
- Limited depth – Vector engraving can generally engrave deeper than raster engraving. This also makes them more vulnerable to wear.
What is Vector Engraving Commonly Used For?

- Logos and branding materials – Business cards, stationery
- Custom signage – Signage for businesses, events, and other applications
- Awards and trophies – Engraving names on trophies, plaques, and medals
- Personalized gifts – Personalized jewelry, keychains, and phone cases
- Etched glassware – Wine and whisky glasses and beer stein glasses, especially if you have a laser engraver with a rotary attachment
- Industrial applications – Engraving serial numbers or part numbers on machinery and equipment
- Architectural applications – Engraving text or designs on metal or wood panels for building facades or interior decor
- Artistic applications – Creating fine art prints or etched metal sculptures
- Customized packaging – Engraving logos or designs on product packaging or gift boxes
What is Raster Engraving Commonly Used For?
- Photographs and other full-color designs
- Detailed illustrations and graphics
- Personalized gifts – Personalized photo frames, mugs, and phone cases
- Customized promotional items – Customized keychains, pens, and USB drives
- Artistic applications – Creating mixed media pieces or engraved paintings
- Textures and patterns – Engraving wood grain or stone textures
- Industrial applications – Engraving logos or designs on metal parts or machinery
- Architectural applications – Engraving designs or patterns on glass panels or doors
- Packaging and product labeling – Creating engraved labels for wine bottles or food packaging
Vector or Raster Engraving: Which to Choose?
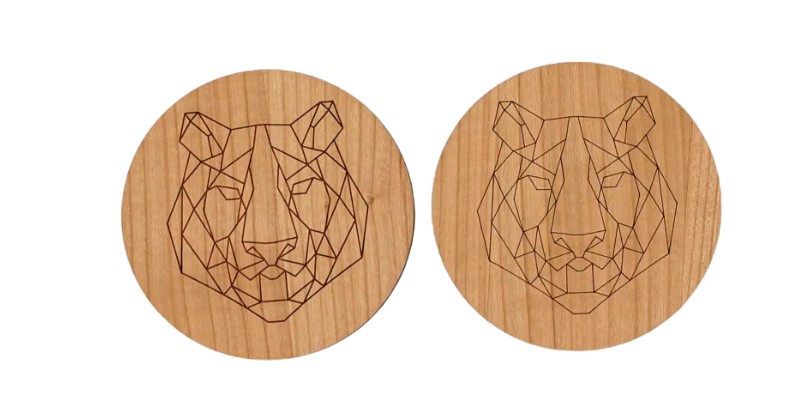

Deciding on whether to choose vector or raster engraving depends on what you want to create.
Vector engraving is better suited for when you want greater speed, and when outlines and drawings suffice.
However, raster engraving is better if you need to fill in the image, give varying lightness and darkness within colors, or want to show texture.
Tips for the Best Results when Raster Engraving
- Choose the right material – Leather, wood, and acrylic are some great options.
- Ensure the raster image is optimized – If it’s an image, use appropriate contrast and brightness along with grayscale threshold. If switching a vector design into a raster, use enough resolution.
- Use the right settings – The settings for your laser power, resolution, and speed will all affect the overall quality of the engraving. Go too fast, for example, and you won’t engrave the darkest parts of your design well (unless your laser is super powerful).
- Keep the machine clean – Good machine maintenance is essential for the best results. Having a clean workspace makes this significantly easier.
- Test your settings – Testing your laser settings on a small piece of material will minimize the risk of you wasting material.
- Use the right line spacing – Overlapping can result in uneven lines when raster engraving. Space your lines correctly and ensure your artwork is optimized.
Tips for the Best Results when Vector Engraving
- Choose the right material – Wood, acrylic, and some metals are best for vector engraving.
- Clean the material – Cleaning the material to remove dirt or dust minimizes the risk of interference.
- Choose the right settings – Ensure you have the optimal settings for the design and materials you are using.
- Optimize the design – Pick high-quality raster images that’ll lead to a good-looking final engraving with precise details.
- Ventilate the area properly – Vector engraving can result in smoke or fumes. Proper ventilation is essential to this process, and air assist is helpful.
FAQs
Can raster images be converted to vector images?
Yes, you can use tools such as Adobe Illustrator’s Image Trace tool to convert a raster image into a vector image. This will allow you to expand the applicability of the image without data degradation.
How are vector graphics and raster graphics produced?
Raster images are created using dots or pixels. Vector images are created using geometric formulas that create lines and shapes.
Can I use vector or raster engraving on all materials?
No, there are certain materials that should not be cut. Certain materials like PVC or coated carbon fiber can emit noxious fumes. Other materials like polystyrene and HDPE have the potential of melting or catching on fire and should be avoided.
Always check the material you intend to use is safe to do so.
But, there aren’t any materials that you can raster engrave but not vector engrave on, and vice versa. The above-mentioned materials are just those that you should never do any form of laser engraving on.
Final Thoughts
Both vector and raster engraving have their pros and cons and are best suited to certain applications.
Raster engraving is better suited to full-color projects, textured engraving, large-area printing, bold texts, logos and filled areas.
For a precise, smooth engraving of curves, contours, and outlines, vector engraving is the most suitable.
Taking the time to look at both laser engraving options and the applications you want to use them for will help you make the right decision.