Key Takeaways
- Laser vs Hand Engraving: Laser engraving is faster, more precise, and easier than hand engraving, but has some limitations.
- 3D Engraving: Hand engraving can create more depth and 3D effects than laser engraving, which is mostly 2D.
- Material Size: Hand engraving can work on any material size, shape, and weight, while laser engraving is restricted by the machine’s working area.
- Applications: Laser engraving is widely used for industrial and personal purposes, while hand engraving is more suitable for artistic and unique projects.
Laser engraving is more accessible, much faster, requires less technical skill than hand engraving. It’s also bettter for engraving precision designs and is a popular choice for industrial applications due to its consistency and speed.
However, hand engraving outperforms laser engraving in 3D engraving, providing depth that can’t be achieved by lasers. You can work working on a wider range of material sizes, weights, orientations, and on-site engraving where lasers would not work. Also, the cutting depth, embossing capabilities, and durability of hand-engraved pieces outperform lasers.
You might think hand engraving is dead because of modern laser engravers, but that’s simply not true. I have close-up experiences with hand engraving and have personally compared hand-engraved with laser designs – and I’ll report my findings on the differences in this article.
Hand Vs Laser Engraving: A Quick Summary
Overall, laser engraving is better for most practical uses, such as engraving on metals and wood, due to its precision and speed.
However, hand engraving offer certain advantages, such as for engraving on stone (unless it’s for engraving an image), or dealing with immobile objects or objects that are too large or tall to accommodate a laser machine.
| Laser engraving | Hand engraving | |
|---|---|---|
| Easy to do | ✔ | ❌ |
| Contrast | ✔ | ❌ |
| Extremely fine engraving | ✔ | ❌ |
| Tremendous detail | ✔ | ❌ |
| Image engraving | ✔ | ❌ |
| Faster engraving (some exceptions) | ✔ | ❌ |
| Industrial use | ✔ | ❌ |
| Annealing | ✔ | ❌ |
| Large materials | ❌ | ✔ |
| On-sight engraving | ❌ | ✔ |
| 3D engraving | ❌ (very limited) | ✔ |
| Deep engraving | ❌ | ✔ |
| Embossing | ❌ | ✔ |
| Various edge angles | ❌ | ✔ |
| Irregular surfaces | ❌ | ✔ |
| Durability | Durable | Very durable |
| Engraving Cost | Low | High |
Hand engraving also remains a popular choice for certain types of jewelry engraving and sculptures, where the artisanal, personal touch and the more depth and 3D options can make for some unique effects.
What is Laser Engraving?
Laser engraving is a hands-off approach to engraving: you use control software, such as Lightburn, to move a laser beam over a piece of material based on your design.
You can either design the engraving or cutting design in vector software like Photoshop or Inkscape, or import images for raster engraving into the software, and you can engrave anything from images, to text, to any other design, and the laser will engrave similar to how an inkjet printer would.
What is Hand Engraving?
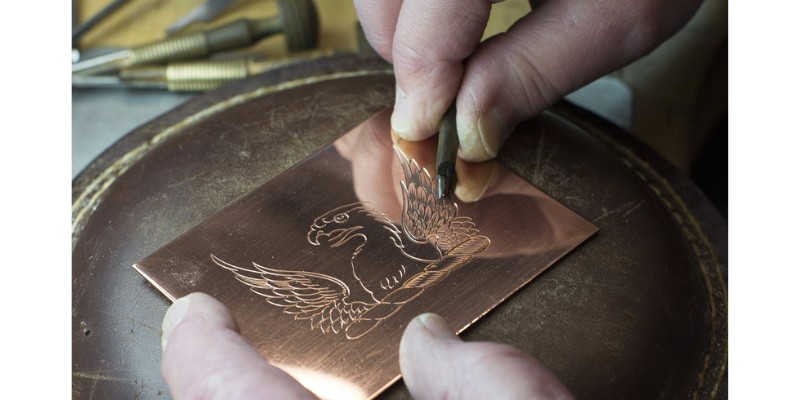

While laser engraving is a comparatively new technology, first commercialized in the 1960s, hand engraving dates all the way back to the new Stone Age.
Hand engraving involves inscribing a design onto a material using a hand-held tool. The tools used can include a graver (also known as a burin), an engraving pen, a grinder, or a handheld router.
This is mostly done free-hand, but can sometimes involve stencils and guides to ensure precision. The hand engraver uses equipment to securely the material down during the engraving process.
While laser engraving takes minimal time to learn, engraving by hand takes years to master. Being less precise than laser engraving, hand-engraved pieces are considered more unique.
It’s worth noting, however, that handheld lasers – while technically operated by hand – are often categorized under laser engraving as they use laser technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser and Hand Engraving
Laser Engraving Advantages
Here are the pros of laser engraving:
- Easier to learn than hand engraving
- Faster
- Grayscale engraving options for images
- High contrast engraving options
- Fine and detailed engraving
- Industrial use and more scalable
- Can etch and anneal
- Cheap engraving cost, especially for batch engraving
Laser Engraving Disadvantages
Despite being the modern method, laser engraving also has many cons:
- Can’t engrave 3D (very limited 3D capabilities)
- Can’t emboss (very limited embossing)
- Can’t engrave irregular surfaces
- Can’t vary the engraving’s edge angle
- Can’t engrave large materials
- Limited depth compared to hand engraving
- Higher equipment cost
Hand Engraving Advantages
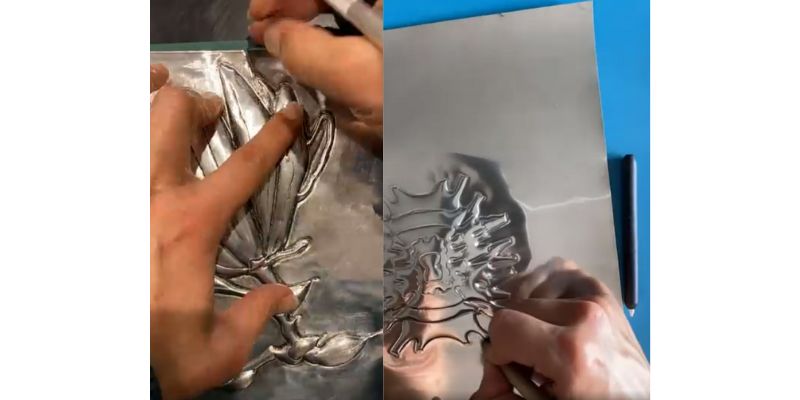

Despite being an ancient technique, hand engraving has many advantages over lasers:
- 3D engraving metals and most materials
- Embossing
- Engraving large material and onsight engraving
- Engrave all material sides and irregular surfaces
- Sloped engraving edges possible
- Deep engraving
- Generally more durable
Hand Engraving Disadvantages
- Difficult to master
- Costly (labor Intensive)
- Slow
- Unsuitable for fine designs (not as accurate as lasers)
- Can’t create photorealistic images like lasers
Differences: Laser Engraving vs Hand Engraving
Uses and applications
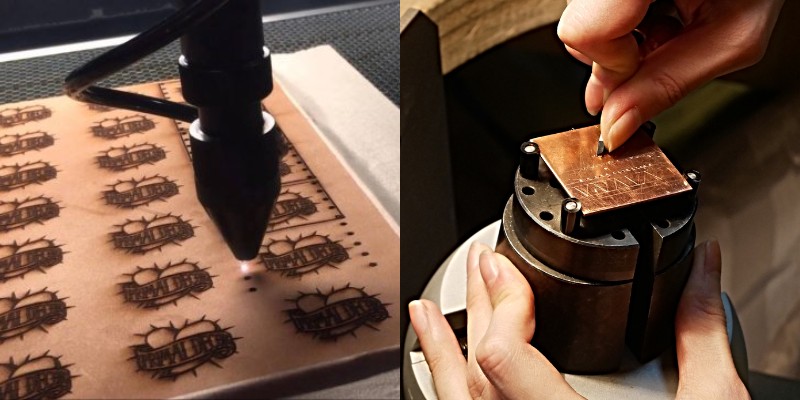

Laser engraving is much more efficient than hand engraving. As a result, it’s used in industry to engrave barcodes, part numbers, and other information. It’s also used in engraving jewelry.
Beyond industrial uses, laser engraving is heavily used for personalizing items and creating decorative pieces and art. The ability to engrave intricate designs and images has created a flourishing market platforms like Etsy for laser-engraved items, including wooden wall art, coasters, clocks, custom cutting boards, wedding gifts, pet accessories, and other decor.
Hand engraving is instead often used for creating unique, one-of-a-kind items. Its applications include engraving commemorative items (like stones), crafting jewelry, engraving precious stones, and designing specific decorative items like clocks.
The personal, artisanal touch of hand engraving is often chosen for high-profile events like Wimbledon, the Claret Jug, and the Stanley Cup, where the winners’ trophies are engraved by hand on site.
Ability to create contrast
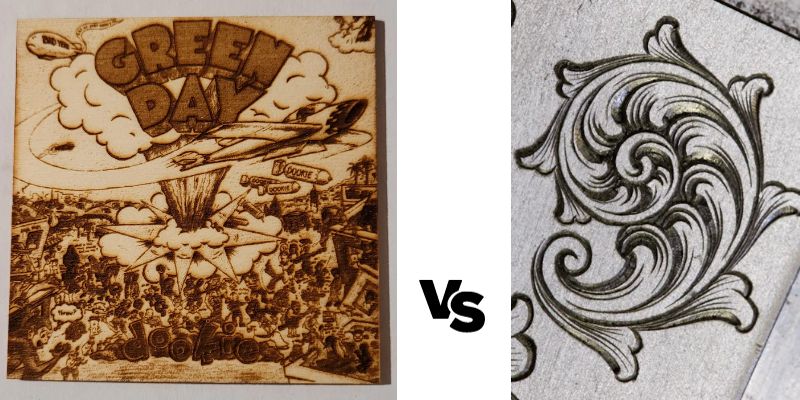

A major advantage of laser engravers is the ability to create as much contrast as you want on images and other design projects. Especially on wood, you can reduce laser speeds to create a darker color in certain areas to create a 3D effect and adding depth to yours designs.
Beyond this, laser engravers and etching machines often etch with high contrast, but this can be reduced in your settings.
Hand engraving, however, doesn’t naturally create much contrast, particularly on uncoated or unpainted surfaces. Though, the deep cavities created during hand engraving can be filled with paint or other materials, to then create high-contrast designs.
Fine engraving and precise detailing

Lasers can engrave extremely fine details, since the laser beam is very narrow and computer-controlled.
The high contrast produced by laser engraving also renders these fine engravings vividly visible, making it ideal for applications like barcodes and intricate designs.
However, hand engraving can’t accomplish this level of detail due to the limits of human dexterity.
In comparison, hand engraving cannot achieve the same level of detail due to the limits of human dexterity.
An example is the difference between handwriting a page of a book versus printing it with a printer. You just will not achieve the same detail or repeatability by hand, so for these detailed and precise uses, laser engraving is better.
Image engraving
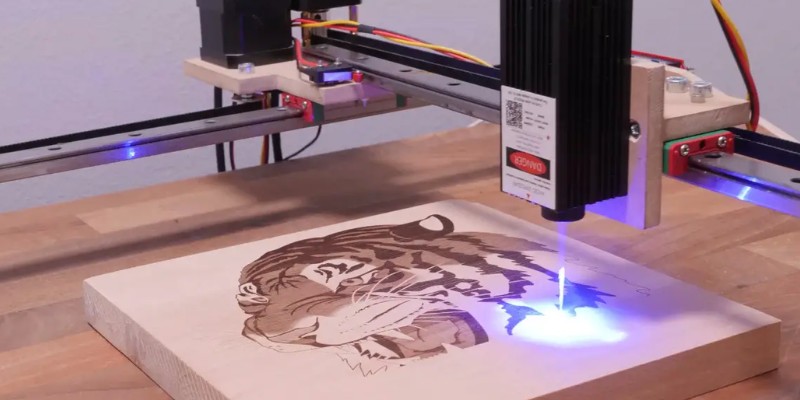

Lasers can engrave grayscale images on various materials due to their high contrast and resolution.
Contrastingly, hand engraving cannot reproduce images in the same way due to its limitations in creating contrast. However, hand engraving does offer a unique advantage in its ability to create 3D drawings or sculptures, which I will discuss more later.
Speed
Laser engraving is significantly faster than hand engraving as it’s guided by computer-controlled instructions from your software, and lasers can move in excess of several meters per minute.
For example, laser machines can swiftly engrave complex patterns on jewelry within minutes, while a similar hand engraving projects could take hours or even days, depending on the detail level. It also depends on the artist’s skill and speed, and the specifics of the project to be hand engraved.
Annealing
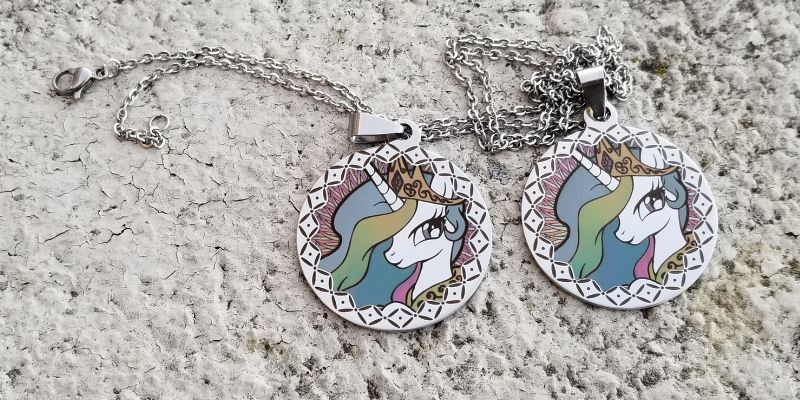
Annealing is another technique, where instead of physically removing material, lasers can heat certain metals to create visible marks via chemical reactions. This is particularly useful with stainless steel since it preserves its anti-corrosive properties. While not technically engraving, annealing is worth noting as it’s within the laser domain.
Hand engraving involves physically removing material using a hand tool, in contrast to the heat-induced chemical changes lasers can generate during annealing. As such, it’s impossible to retain stainless steel’s anti-corrosive properties like you can with stainless steel – which is another benefit that lasers have over hand engraving.
Large-scale engraving

A laser engraver’s working area limits the size it can engrave. And not just the width and length, but also the height, as you can’t put materials that are too tall into the machine.
A major advantage of hand engraving over lasers is you are not limited by material size. I’ve personally seen hand engravers sit on large cubic stones and engrave fine designs.
It’s also about the material’s weight. Some materials are too heavy or large to move, so you obviously can’t put these in a laser.
Hand engravers are not tied down, and can be moved to where the object is. In this case of the large cubic stone, I saw the hand engraver working on it on-site.
3D engraving
Hand engraving is naturally capable of crafting 3D engravings. For example, skilled hand engravers can sculpt 3D forms on items like coins.
While lasers can produce 3D patterns on specific woods such as Maple, their 3D engraving capabilities are restricted. The process works on only a few materials, mostly certain wood types, and offers limited depth.
Plus, laser-engraved items often require a lot of post-processing due to charring, adding to the time it takes to produce a finished, presentable piece. Though, you can reduce charring with air assist.
Given these limits, lasers are mostly considered 2D engravers. When it comes to 3D designs, hand engraving generally offers greater options than laser engraving.

Deep engraving

Lasers typically can’t engrave very deep, especially on harder materials like metal, though they can cut through fairly thick wood and acrylic sheets.
For example, on metals, most laser engravers can only achieve engraving depths between 0.05 and 0.5mm on metals.
In contrast, hand engraving allows for carving significantly deeper into the material, with the ability to create a more pronounced 3D effect in the material.
Embossing / Raised letters
Hand engraving is capable of embossing, where a design or text is made to stand out above the surface. For example, when embossing text, the engraver carves away the areas surrounding the letters, leaving the text itself raised above the surface.
This technique can be accomplished with hand engraving tools (and CNC machines!), but is not well-suited to laser engraving.
While lasers can mimic embossing effects on materials that they can 3D engrave, these capabilities are very limited.

Angled engravings – such as sloped letter cavities
Laser engraving creates cavities that are perpendicular to the surface, since the laser beam points down and penetrates straight into the material.
In contrast, with hand engraving you can alter the angle of your cut. As shown in the image below, the hand engraver has achieved an angled engraving where the edges of the letter slant into the material, meeting at a valley point.
This ability to control the angle of engraving is a distinct advantage of hand engraving.

Irregular Surfaces
By default, laser engravers can only work on flat surfaces, but if you add a rotary attachment you can also engrave on cylindrical objects. Beyond this, lasers cannot engrave irregular surfaces – only those that are flat or cylindrical.
In contrast, hand engraving offers the flexibility to work on any surface. This makes hand engraving more versatile for certain uses.
For instance, the irregular surface in the image below could not be worked on by any laser engraver in the world, while a skilled hand engraver could work on it and create intricate 3D patterns.

This is also beneficial when engraving natural stones. While the stone’s surface may be uneven, it can still be engraved by hand. Plus, hand engravers can engrave natural stone from all angles.
Durability
The durability of an engraving depends on the hardness of the material being engraved, and the depth that the engraving reaches. Although laser engravings are generally quite durable, since hand engravings are typically deeper, they can offer more longevity.
Though, both methods offer durable results with the right settings on the right materials.
Price
Hand engraving is generally more expensive than laser engraving. Despite the up-front investment buying the laser machine, the increased speed and efficiency of laser engraving lowers costs per item, particularly for larger orders.
Although the cost difference for a single item may be marginal, the cost of laser engraving per item for larger orders falls tremendously. In other words, laser engraving 100 items with the same design is significantly cheaper than hand engraving.
For more information on the prices of laser engraving, we have an article on how much a laser cutter costs.